Nessus简介
Nessus 是一款广泛使用的网络安全扫描工具,由 Tenable, Inc. 开发和维护。它专注于进行漏洞扫描和合规性审计,以帮助组织识别和解决其 IT 基础设施中的安全漏洞。Nessus 主要用于以下目的:
漏洞扫描:
扫描网络设备、服务器、虚拟机、数据库和其他 IT 资产中的已知漏洞。支持多种协议和服务的安全检查,包括 HTTP、FTP、SSH、DNS 等。
配置审计:
检测 IT 系统中的不安全配置,确保符合安全基准和最佳实践。
恶意软件扫描:
查找潜在的后门、恶意软件和其他安全威胁。
合规性审计:
评估系统是否符合特定的安全政策和法规,如 PCI DSS、HIPAA、NIST 等。
敏感数据检测:
扫描存储和传输中的敏感数据,如信用卡号和个人身份信息 (PII)。
工作原理
Nessus 使用插件(Plugins)系统进行扫描,每个插件包含检测特定漏洞或配置问题的指令。扫描时,Nessus 会连接到目标网络,并基于选定的扫描模板和策略, 发送请求和进行分析。Nessus 插件数据库经常更新,以确保它能够检测到最新的漏洞。
Nessus 主要有以下版本:
Nessus Essentials:免费版本,适用于个人和小型组织,功能有限。
Nessus Professional:付费版本,适用于专业安全测试人员和中小型企业,提供更广泛的功能和支持。
Nessus Expert:扩展了功能,如云环境扫描、容器化应用检测等。
Tenable.io 和 Tenable.sc:更高级的产品,提供企业级的漏洞管理解决方案和集成分析。
优点
易于使用:直观的界面和丰富的模板,用户可以快速上手。
插件更新:定期更新插件库,确保扫描工具始终能检测到最新的威胁。
定制化扫描:用户可以根据具体需求定制扫描任务和报告。
使用场景
企业定期进行的安全审计和风险评估。
安全团队用来识别和修复新发现的漏洞。
合规性检查以确保满足法规要求。
安全工程师和渗透测试人员进行的网络评估和测试。
Nessus 是全球最受欢迎的漏洞扫描工具之一,因其高效的检测能力和易用性,在安全行业中被广泛使用。
代码目录结构
|- export_report
|- config (配置文件目录)
| └── config.ini (核心的配置文件)
|- scripts (脚本目录)
| └── send_report.sh (发送生成文件的bash脚本)
|- main.py (通过NessusApi生成HTML的python文件)
|- nessus_api.py (NessusApi的函数python文件)
|- utils.py (工具python文件)
|- html (HTML存储目录)
相关代码内容
config
config.ini
[NessusInfo]
; nessus的访问站点
website = nessus的访问站点
; api的ak
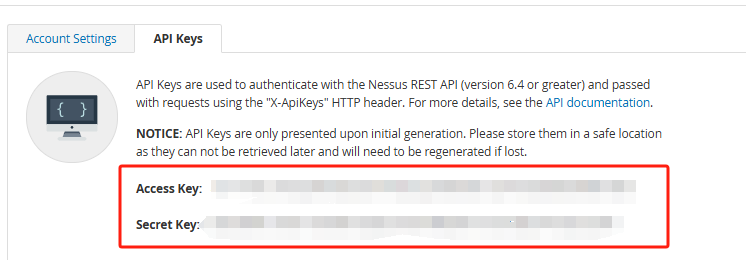
accessKey = nessus生成的 accessKey
; api的ak
secretKey = nessus生成的 secretKey
[TaskInfo]
; 扫描任务的接口
get_scan_url=scans
; 导出的HTML的模板ID接口
get_template_url=reports/custom/templates
; 获取最新的扫描记录的接口
scan_url = scans/scan_id?limit=2500&includeHostDetailsForHostDiscovery=true
; 导出报告的接口
export_url = scans/scan_id/export?limit=2500&history_id=scan_result_id
; 下载报告的接口
download_url = scans/scan_id/export/fileId/download
; 是否可以导出的接口
export_status_url = tokens/token_id/status
utils.py
import sys
import requests
import os
import json
# 禁用安全请求警告
from requests.packages import urllib3
from datetime import datetime
import time
import configparser
import re
# 保存为 html的函数
def save_html(content, file_path):
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(content)
# 确认目录是否存在
def ensure_directory_exists(directory_path):
# 检查目录是否存在
if not os.path.exists(directory_path):
# 如果目录不存在,创建它
os.makedirs(directory_path)
# 加载ini配置文件
def load_config(file, module_name):
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(file)
return config[module_name]
# 替换关键字符串的位置
def reg_replace(replace_string, origin_string, new_string):
new_url = re.sub(replace_string, str(new_string), origin_string)
return new_url
nessus_api.py
import requests
import json
# 获取scan_id的接口
def get_scan_id(scanApi,headers):
scan_id=-1
response = requests.get(scanApi,headers=headers, verify=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
scan_id = response.json()['scans'][0]['id']
return scan_id
# 获取自定义模板的接口
def get_template_id(templateApi, headers,template_name='Complete List of Vulnerabilities by Host'):
template_id=-1
response = requests.get(templateApi, headers=headers, verify=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(response.json())
for item in response.json():
if item['name'] == template_name:
template_id = item['id']
break
return template_id
def export_api(export_url,template_id,headers):
result=[]
# 导出的载荷模板
payload = json.dumps({
"format": "html",
"template_id": template_id,
"csvColumns": {},
"formattingOptions": {},
"extraFilters": {
"host_ids": [],
"plugin_ids": []
},
"plugin_detail_locale": "en"
})
export_res = requests.post(export_url, headers=headers, data=payload, verify=False)
if export_res.status_code == 200:
result = export_res
return result
else:
return result
main.py
import sys
import requests
import os
import json
# 禁用安全请求警告
from requests.packages import urllib3
from datetime import datetime,timedelta
import time
import configparser
import re
import subprocess
from utils import *
from nessus_api import get_scan_id,get_template_id,export_api
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 禁用安全请求警告
urllib3.disable_warnings()
file_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
config_file = os.path.join(file_path, 'config', 'config.ini')
script_file = os.path.join(file_path, 'scripts', 'send_report.sh')
#集成告警媒介的一段代码
#dingding_notice_file = os.path.join(file_path, 'scripts', 'omc_dingding.py')
# 判断生成html 文件的目录是否有存在, 如果不存在就手动创建
ensure_directory_exists(os.path.join(file_path, "html"))
# 获取 ak sk
nessusInfo = load_config(config_file, "NessusInfo")
website=nessusInfo['website']
ak = nessusInfo['accessKey']
sk = nessusInfo['secretKey']
# 如果获取失败, 打印相关的ak sk 看看是否正常读取
# print(f"ak:{ak};sk:{sk}")
token = f"accessKey={ak}; secretKey={sk}"
# 请求头最新的数据
headers = {
"X-ApiKeys": token,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
# 读取相关的配置文件的内容
TaskInfo_data = load_config(config_file, "TaskInfo")
get_scan_url = website+'/'+TaskInfo_data['get_scan_url']
get_template_url = website+'/'+TaskInfo_data['get_template_url']
scan_url = website+'/'+TaskInfo_data['scan_url']
download_url = website+'/'+TaskInfo_data['download_url']
export_url = website+'/'+TaskInfo_data['export_url']
export_status_url = website+'/'+TaskInfo_data['export_status_url']
scan_id=get_scan_id(get_scan_url,headers)
template_id=get_template_id(get_template_url,headers)
if scan_id == -1 or template_id == -1:
sys.exit(-1)
scan_url = reg_replace("scan_id", scan_url, scan_id)
# 发送POST请求导出报告
response = requests.get(scan_url, headers=headers, verify=False)
scan_result=[]
last_history_record={}
if response.status_code == 200 :
scan_result = json.loads(response.text)
if len(scan_result)>0:
if len(scan_result['history']) > 0:
# 获取 扫描记录的 last_history_record 判断 最新的扫描任务是否完成
if scan_result['history'][-1]['status'] == 'completed':
last_history_record = scan_result['history'][-1]
else:
# 说明还没有扫描完成
print("没有扫描完成")
sys.exit(-1)
else:
# 说明没有扫描记录文件
print("没有获取到报告")
sys.exit(-1)
print(last_history_record)
last_history_id=last_history_record['history_id']
# 获取最新的扫描记录的时间 , 并转换为北京时间
utc_time = datetime.utcfromtimestamp(last_history_record['last_modification_date'])
beijing_time = utc_time + timedelta(hours=8)
formatted_time = beijing_time.strftime('%Y%m%d')
# 发送POST请求导出报告
export_url=reg_replace("scan_result_id", export_url, last_history_id)
export_url = reg_replace("scan_id", export_url, scan_id)
print(f"export_url:{export_url}")
export_res=export_api(export_url, template_id,headers)
export_result=[]
fileId=000
if export_res.status_code == 200:
export_result =json.loads(export_res.text)
fileId=export_result['file']
token_id=export_result['token']
# 发送GET请求下载文件
download_url = reg_replace("fileId", download_url, fileId)
download_url = reg_replace("scan_id", download_url, scan_id)
export_status_url= reg_replace("token_id", export_status_url, token_id)
while True:
response = requests.get(export_status_url, headers=headers, verify=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
try:
data = json.loads(response.content)
if data.get('status') == 'ready':
print('下载已准备好!')
break
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print('返回的响应无法解析为 JSON。')
else:
print(f'请求失败,状态码:{response.status_code}')
print(f'响应内容:{response.content}')
# 等待 3 秒再进行下一次请求
time.sleep(3)
print('可以下载文件了。')
res = requests.get(download_url, headers=headers,verify=False)
filename = os.path.join(os.path.join(file_path, "html"), f"{formatted_time}.html")
# 检查响应状态码是否为200,表示请求成功
if res.status_code == 200:
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(res.content)
print("文件已保存到:", filename)
else:
print("下载失败:", res.status_code)
# # 调用脚本将生成的html文件传送到相关的位置归档
subprocess.run(["/bin/bash", script_file, ])
scripts
send_report.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 传入的文件名称
file_name=${1}
# 远程传输的目录 远端的服务器需要做 SSH免密登录
remote_port= ssh端口
remote_host= ssh主机
remote_user= ssh用户
remote_path= ssh目录
if [ -d $file_dir ];then
if [ -f $file_name ];then
scp -P$remote_port $file_name $remote_user@$remote_host:$remote_path
echo "send success"
else
echo "$file_name not exist"
exit -2
fi
else
echo "$file_dir not exist"
exit -1
fi
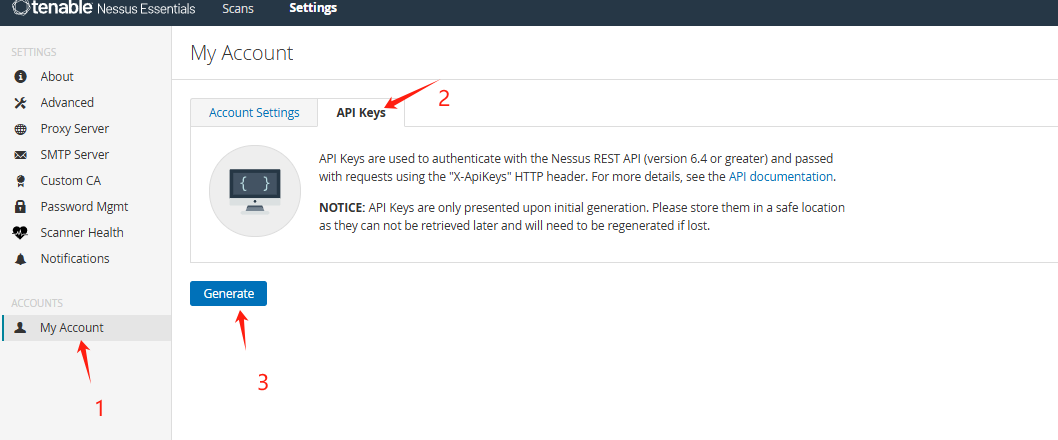
附录:Nessus生成AKSK的方法